C# Real Time Programming
Triamec servo drives, I/O controllers and adapters are freely programmable for customer-specific applications. Two tasks are available for this purpose:
- Isochronous task in 10kHz
- Asynchronous Task
Development is done with Microsoft Visual Studio in C#, which translates the code into the intermediate language CIL. A virtual machine (TamaVM) is installed on the Triamec devices, which interprets this standardized language and executes it in real time.
A Tama program can be loaded into the devices at runtime and then executed. For stand-alone applications without PC connection Tama programs can be stored persistently in the devices. Tama programs have access to all registers of the executing device and to cyclically transmitted coupling data of other devices.
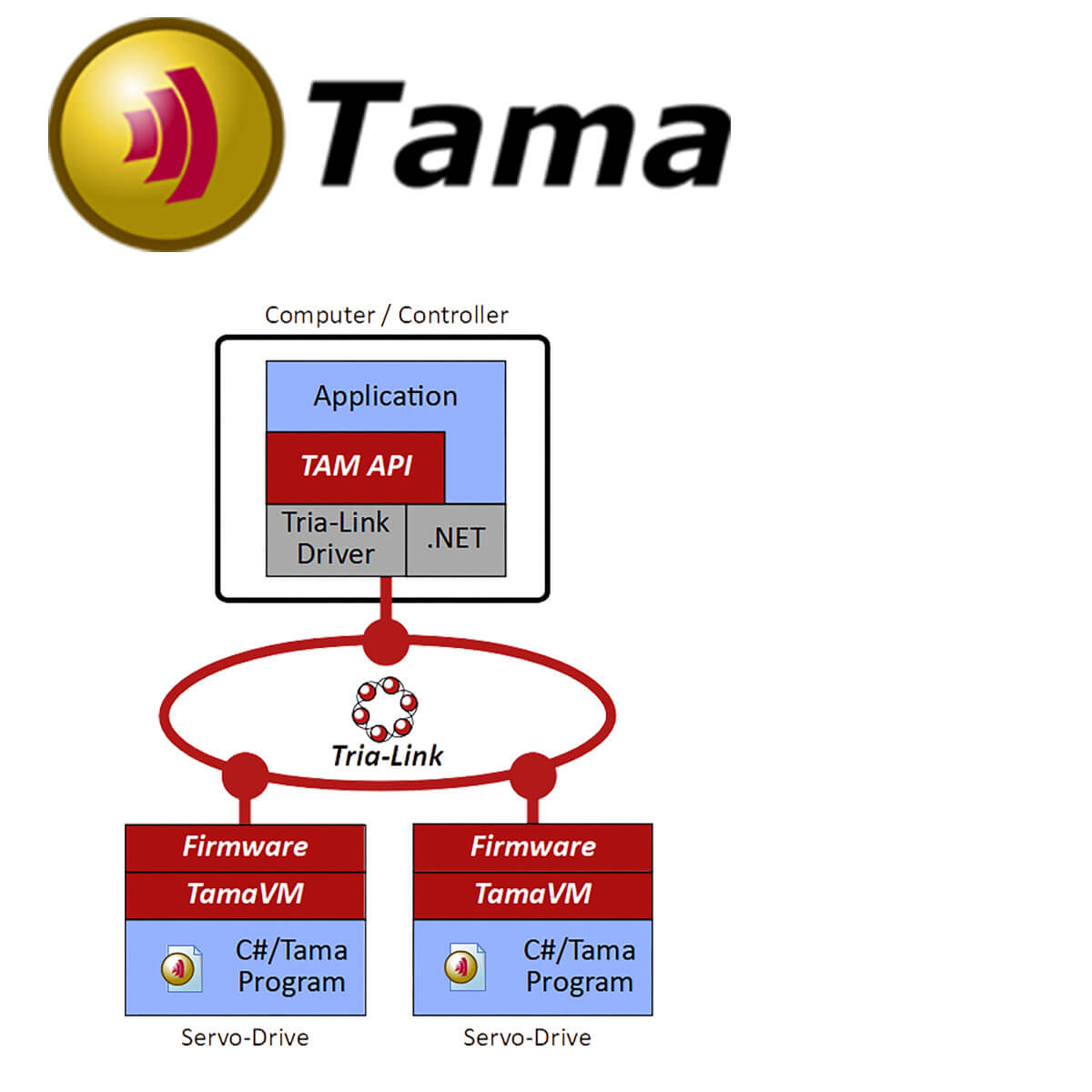

Key features
Robust runtime environment: Virtual machine inside the device ("crash-proof")
Two tasks: One 10kHz real-time and one asynchronous task
Hard real-time in 10kHz
Strict type safety
Data types: int, float, bool, enum, struct, object, array
Access to device registers with IntelliSense function of Visual Studio
Mathematical functions
Interaction with PC application or Tama programs on other devices
New programs can be loaded and executed at runtime
Persistence allows autonomous operation without PC
Applications
Tama programs enable advanced motion control functionality directly on the servo drive. Typical applications include homing sequences and touch detection for precise positioning, axis couplings for synchronized portal systems, and kinematics calculations for complex mechanisms such as parallel kinematics in delta robots.
Tama supports sequence controls for simple stand-alone applications like force-guided presses, dual loop control implementations that can integrate with other servo drives, and parameter adaptation for control optimization through gain scheduling. The platform also handles monitoring functions and other real-time machine reactions that require immediate response without external controller overhead.
Programming
Tama programs are developed in C# using Visual Studio®. Programs run on all Triamec servo drives.
Documentation and resources
The Tama User Manual is available in the Manuals section.
Templates and example programs are available on GitHub, tagged with the Tama badge for easy identification.
Sample program
The following example demonstrates basic Tama programming principles through a simple isochronous task, showing how to access drive registers and implement core functionality.
using Triamec.Tama.Rlid19; // required for register access
using Triamec.Tama.Vmid5; // required for interpretation of Tama task attributes
[Tama] // attribute to indicate the starting point for the Tama compiler
static class D1_MinimalTama // name of the tama program
{
/*****************************************************************
* members
*****************************************************************/
static float actualPosition;
/*****************************************************************
* isochronous main task
*****************************************************************/
[TamaTask(Task.IsochronousMain)] // attribute to indicate the entry point and the task type
static void Main() // main function, name is not relevant
{
// your code
actualPosition = (float)Register.Axes_0.Signals.PositionController.MasterPosition; // type of position is doup
Register.Application.Variables.Floats[0] = actualPosition; // use a generic register to display the position
Register.Application.Variables.Booleans[1] = Register.Application.Variables.Booleans[0]; // reflect boolean 0 to boolean 1
}
}


